The heart
12 July 2007
The heart is a large, hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood filled with oxygen and nutrients through the blood vessels to the body tissues. The heart is located in the centre of the chest, slightly towards the left, and is about the size of the child’s fist.
Normal Circulation
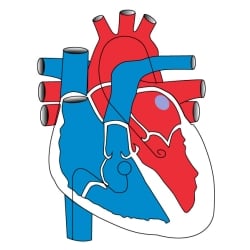
- Blood, depleted of oxygen due to the metabolic needs of the body, returns from the body to the heart through two large veins, the superior vena cava (1) and inferior vena cava (2).
- This “blue”, or deoxygenated, blood enters the right atrium (3).
- Blood then travels through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle (4).
- The right ventricle ejects this volume of blood through the pulmonary valve and pulmonary artery (5) into the lungs.
- Gas exchange occurs in the lungs. There the blood picks up oxygen and rids itself of carbon dioxide.
- This oxygenated or “red” blood then returns by the pulmonary veins (6) and collects in the left atrium.
- It then passes through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle. (8)
- From there it is pumped by the left ventricle through the aortic valve into the aorta (9), which takes oxygenated “red” blood to the body.
This page needs an update? Report it here!
